143 results
Investigation of the Natural Progression of Clonal Hematopoiesis of Indeterminate Potential and Clonal Cytopenia of Undetermined Significance
Doctors at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) are conducting a study on patients with Clonal Cytopenia of Uncertain Significance (CCUS). Patients with CCUS have low blood counts and a normal bone marrow exam but more advanced genetic testing shows the presence of a genetic mutation that is likely causing the low counts. The study will look at CCUS and try to determine its relationship to blood cancers and heart disease. The study will also try to discover other new organs or diseases it may be linked with.
Learn More

Investigation of the Natural Progression of Clonal Hematopoiesis of Indeterminate Potential and Clonal Cytopenia of Undetermined Significance
Doctors at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) are conducting a study on patients with clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP). Patients with CHIP have a genetic mutation that has been associated with blood cancer. The study will look at CHIP and try to determine its relationship to blood cancers and heart disease. The study will also try to discover other new organs or diseases that may be linked with.
Learn More

Pilot Study for Geospatial Analysis of Neighborhood Environmental Stress in Relation to Biological Markers of Cardiovascular Health and Health Behaviors in Women
Does your pace of life in the city affect your health? Researchers at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) are conducting a study of two neighborhoods in Washington, D.C. in relationship to the environmental stress and the health behaviors of White and African American women. This research study will work to determine if there is a significant connection between neighborhood environment and the impact in women's health.
Learn More
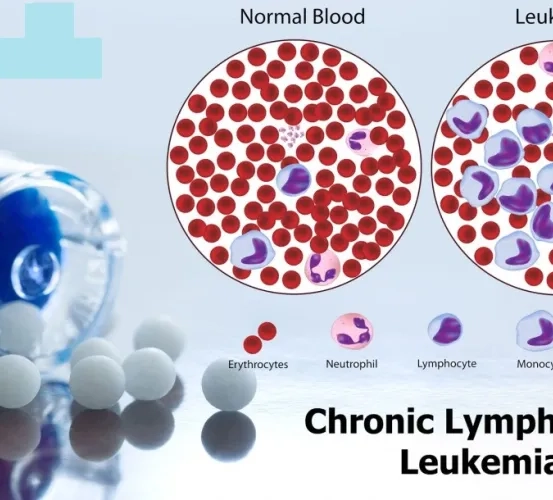
Early Clonal Dynamics During Venetoclax Treatment for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
The research study sets out to learn about changes in the genetic makeup of CLL during the early phase of treatment with venetoclax. The initial phase of venetoclax therapy can be medically and logistically challenging. Patients will receive expert medical care at the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
Learn More

Hígado graso no alcohólico, respuesta hepática a la glucosa oral y efecto de la semaglutida (NAFLD HEROES)
¿Está buscando un tratamiento para su condición de hígado graso no alcohólico (NAFLD, por sus siglas en inglés) o para la esteatohepatitis no alcohólica (NASH, por sus siglas en inglés)? Investigadores de los Institutos Nacionales de la Salud, buscan voluntarios para participar en este estudio. Por 30 semanas, los participantes recibirán semaglutide (medicina usada para la diabetes tipo 2), esto podría mejorar su hígado y ayudarle a perder peso. El estudio espera entender mejor el daño del hígado y los mejores tratamientos para las personas con estas condiciones.
Learn More

Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, the Hepatic Response to Oral Glucose, and the Effect of Semaglutide (NAFLD HEROES) (En español)
Are you looking for a treatment for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) or non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)? Researchers at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) seek volunteers to participate in a research study. For 30 weeks, participants will receive a medication called semaglutide (typically used for Type 2 diabetes), aiming to improve their liver disease and help them lose weight. The study hopes to better understand liver damage and its treatment in people with these conditions. (En español)
Learn More
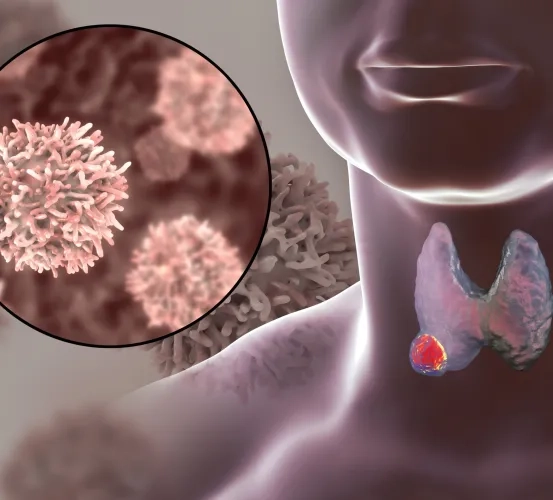
The Use of 124-I-PET/CT Whole Body and Lesional Dosimetry in Differentiated Thyroid Cancer
Doctors at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) seek patients with thyroid cancer that spread outside the thyroid - to the lymph nodes, lungs or bones. The standard treatment in such situation is therapy with radioactive iodine (RAI). In this study, doctors will assess a new imaging tool - 124I PET/CT, which enables evaluation of how much iodine goes into the tumor. The study goal is to compare how much iodine goes into cancer cells after two different methods of stimulation of RAI uptake.
Learn More
An Open-Label Phase 3 Study of the Safety and Efficacy of Pegvisomant in Children with Growth Hormone Excess
Gigantism is a condition characterized by excessive growth and height significantly above average, caused by over-production of growth hormone (GH) during childhood. Investigators at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) want to see if a drug that antagonizes growth hormone action, called pegvisomant, can help children and adolescents with gigantism.
Learn More
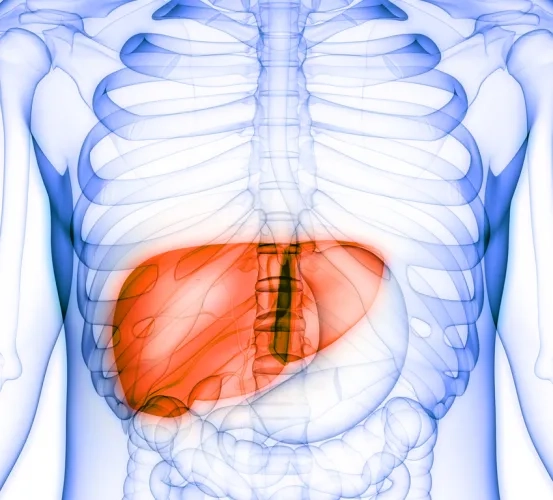
A Phase II Study of Combined Treatment of Durvalumab, Bevacizuamab, Tremelimumab and Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) in Subjects with Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)or Biliary Tract Carcinoma (BTC)
Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC) is the fifth most common cancer in the world. Patients with advanced HCC survive an average of 6 to 9 months. Researchers at the National Institutes of Health are testing the use of an immunotherapy medication called durvalumab, with two other chemotherapy medications, doxorubicin-eluting beads and bevacizumab. This clinical research study will investigate if this combination of medications can stop the progression of HCC.
Learn More

Men at High Genetic Risk for Prostate Cancer
Join a National Institutes of Health (NIH) research study seeking mean men who have a genetic risk factor for developing prostate cancer. Researchers want to follow the prostate health of men who have specific genetic changes associated with prostate cancer to help them learn more about which men are at higher risk for prostate cancer.
Learn More

