NIH Clinical Trial for Relapsed/Refractory B-Cell Malignancies
Collection of Blood, Bone Marrow, and Buccal Mucosa Samples from Healthy Volunteers

Effect of Dietary Omega-7 Palmitoleic Acid-Rich Oil on Lipoprotein Metabolism and Satiety in Adults

Do you or someone you know want to participate in a clinical research study?
Vaccine Responses in Patients with B Cell Malignancies
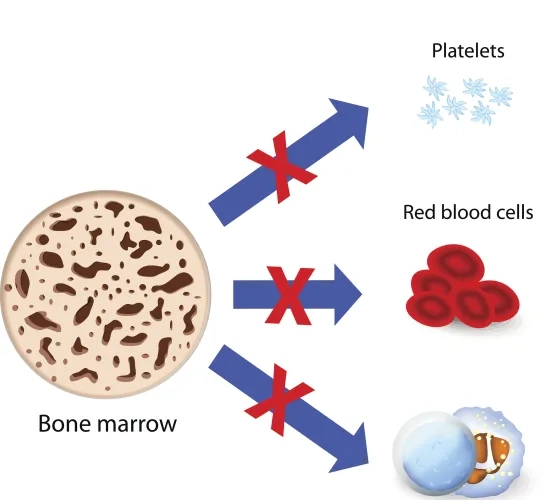
Research Study for Severe Aplastic Anemia (SAA)
Doctors at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) are conducting a research study to determine the viability and safety of early initiation of oral therapy with cyclosporine and eltrombopag in patients with severe aplastic anemia (SAA).

Natural History Study of CADASIL
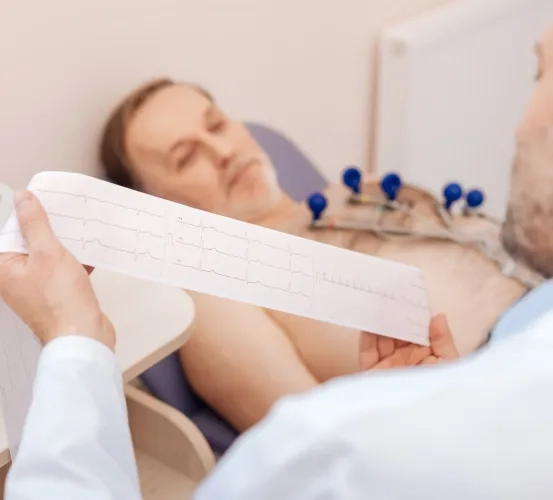
Observational Study of Cardiac Arrhythmias in Subjects Treated with BTK Inhibitors
NIH Tests Fostamatinib for Post-Transplant Cytopenia(s)
After stem cell transplantation, some people develop hard-to-treat anemia (low red blood cells) or thrombocytopenia (low platelets). Cytopenia(s) or low blood cell counts make you weak, prone to bleeding and bruising, and dependent on blood product transfusions. Researchers at the National Institutes of Health (NIH) are testing the drug fostamatinib to see if it is safe to treat cytopenia(s) after stem cell transplantation. A physician referral is not required to participate.


